BPA-Free isn’t What You Think. Here’s The Truth

BPA-free means plastic is safe, right!?
Well, unfortunately, it doesn’t always.
Come to find out, BPA-Free can still mean that other bisphenols were used like BPA and BPF, which are just as harmful.
So we’re here to clear up the confusion and help you understand exactly what it means when a product has this label. We’ll also give you some tips to be sure the product you’re buying is indeed safe.
Let’s get into it!
TL;DR
What Does BPA-Free Mean?
“BPA-free” labels only guarantee the absence of bisphenol A, not safety, as these products can still contain similar bisphenols like BPS or BPF. To stay safe, avoid plastic and choose alternatives like glass, stainless steel, or silicone. Also, be mindful of canned foods, which often contain BPA, and if using plastic, check the recycling codes and avoid codes 3 and 7. Lastly, avoid heating food in plastic containers.
What is BPA?
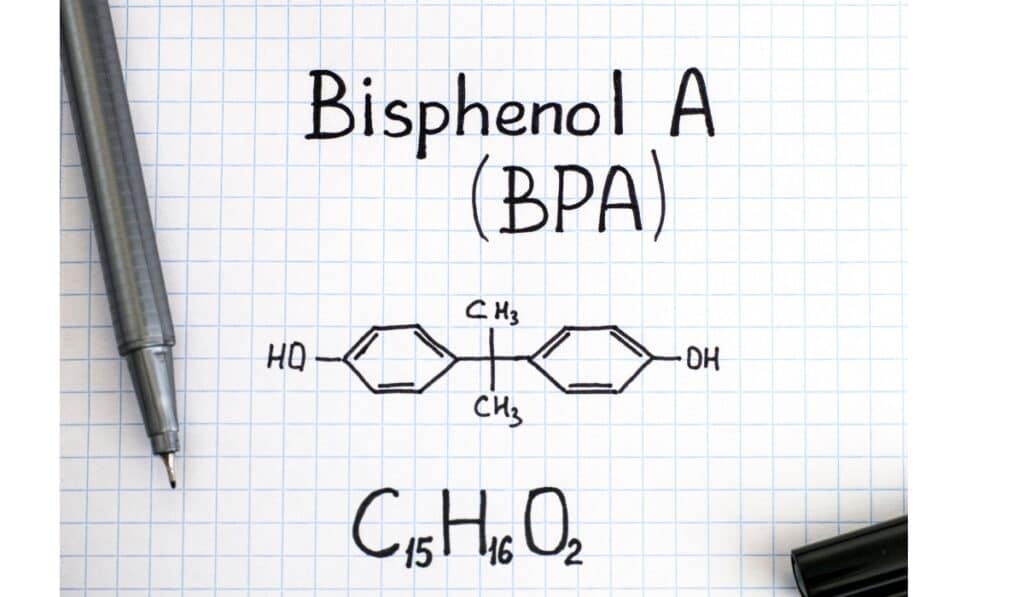
Bisphenol A, commonly known as BPA, is a man-made chemical that has been in use since the 1960s to make certain types of plastics and resins.
It’s used for its ability to make plastics and resins clear, strong, and shatter-resistant.
This is useful in products like water bottles, food containers, and the linings of canned goods, where it helps keep the product safe and durable.
BPA can also be found in many other items, including:
- Dental fillings and sealants
- Medical devices
- Electronics
- Eyeglass lenses
- Sports equipment
- Thermal paper (like receipts)
- Some children’s toys
But why are some products labeled “BPA-free”? Is it dangerous?
Yes, it can be.
Why Is BPA dangerous?
By now, most of us have probably heard about the negative health effects associated with BPA.
BPA is widely known as an “endocrine disruptor” which means it can mimic estrogen. This can interfere with reproduction, increase cancer risk, and cause changes in the immune and nervous system
An article from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) also notes that long-term BPA exposure increases the risk of various diseases and disorders such as:
- Breast Cancer
- Obesity
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Reproductive Disorders
- Testicular Cancer
- Prostate Cancer
And there is no “safe” level of BPA either.
What Does BPA-Free Mean
A product being labeled “BPA-free” only indicates that the item is free of bisphenol a. However, this does not mean the product is safe.
Many BPA-free items might still contain other bisphenols such as BPS or BPF, which have similar effects.
Makes things a bit confusing, right?
What companies did here was switch out BPA for its cousins that are just as bad, all in the name of labeling a product, “BPA-free”.
While I’m sure some companies were unaware of this initially, it’s now no secret that BPA and its alternatives are harmful to human health.
And while some specific plastic types like polypropylene are usually BPA-free, you never really know unless you contact the manufacturer (which just isn’t practical).
So how do we keep ourselves safe?
Here are some tips to make it easy for you.
Tips to Keep Yourself Safe
1. Avoid Plastic
While they might make your life a lot easier, plastics aren’t any good for you or the environment.
This includes bags, Tupperware, Ziploc bags, water bottles, etc. The truth is that if you avoid plastic, you will avoid most sources of BPA and its alternatives.
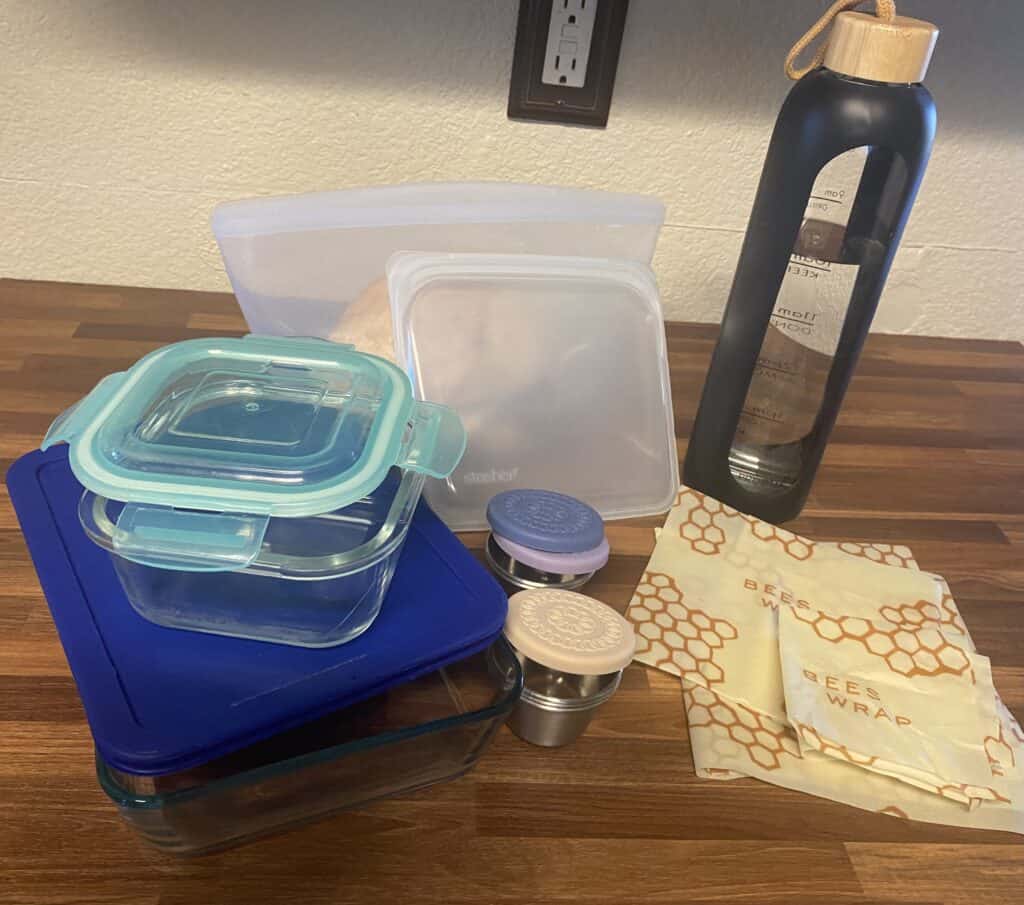
Choose non toxic food storage items such as glass, stainless steel, or silicone, which are naturally free of bisphenols.
Here’s an example of items we replaced our plastic containers with:

2. Avoid Canned Food
Most canned foods have BPA or their substitutes in their lining so if you eat a lot of canned foods, try switching those for fresh or frozen foods.
Remember, shop the outside of the store, not the inside! Packaged food is much more likely to contain BPA.
3. Check The Recycling Code
If you must use plastic containers, check the recycling code on the bottom to ensure you are choosing the safest plastic containers for food storage.
Avoid plastics with recycling codes 3 and 7 as they likely contain BPA.

#3 is also likely to contain phthalates, which you want to avoid as well.
4. Don’t Heat Plastic Containers
Only place cold food in Tupperware/plastic containers and never reheat the food while it is inside.
If you pack food away in a plastic container, transfer it to a non-plastic container when you reheat it.
Thanks for reading! Check out some of our other articles below






